

GITHUB DESKTOP REBASE CURRENT BRANCH CODE
Git is a version control platform which allows several people to work on files simultaneously and push their local copy of the code to the one stored in the cloud. What are all these files, merges, and conflicts? These terms will be unknown to you if you are a beginner in using Git. Error: You need to resolve your current index first This error message also signifies that a merge failed or there are conflicts with the files. What commands or workflows did we miss out? Do you have any suggested tips or tricks too? Let us know in the comments below.The error “ You need to resolve your current index first” occurs in Git and means that there is a merge conflict and unless you resolve the conflict, you will not be allowed to checkout to another branch. There's plenty more to Git than that just these commands. Of course if you're not a command line fan there's plenty of Git UIs you can use: # Reset your current branch to a previous commit and preserve staged local changes # Reset your current branch to a previous commit and preserve all changes as unstaged changes # Reset your current branch to a previous commit and discard all changes since then # Revert a commit by making a new commit which reverses the given
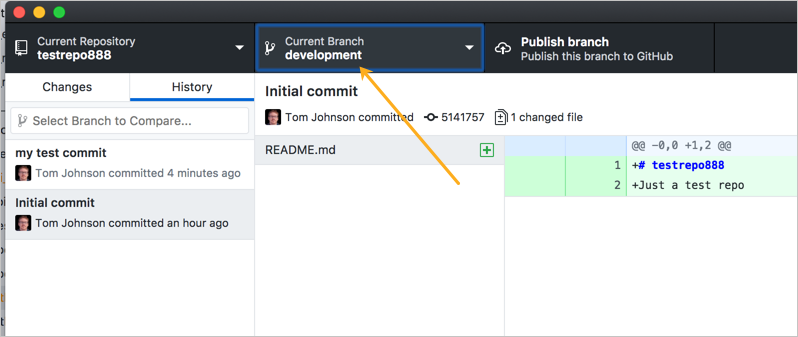
# Discard local changes to a specific file Undo # Discard all local changes and start working on the current branch from the last commit # Use your editor to manually solve conflicts and (after resolving) mark as resolved Git rebase – continue # Use your configured merge tool to solve conflicts # Continue a rebase after resolving conflicts Merge & Rebase # Merge into your current HEAD
GITHUB DESKTOP REBASE CURRENT BRANCH DOWNLOAD
# Download all remote changes and merge them locally # Download all changes from a remote, but don‘t integrate into them locally # Add a new remote at with the given local name # Show who changed each line in a file, when it was changed and the commit id Git log # Show changes over time for a specific file Git commit -m "An inline commit message" # Unstages the file, but preserve its contentsĬommit History # Show all commits, starting from the latest Git commit -am "An inline commit message" # Commit previously staged changes # Commit all local changes in tracked files # Add some changes in to the next commit # Watch these video's for a demo of the power of git add -p. # Add all current changes to the next commit # View changes between staged files and the latest committed version # View changes between staged files and unstaged changes in files Local Changes # List all new or modified files - showing which are to staged to be commited and which are not Git checkout -track origin/feature-branch-foo
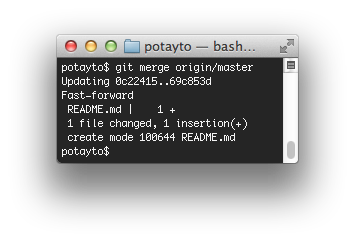
# for example track the remote branch named feature-branch-foo # Create a new tracking branch based on a remote branch # Create a new branch based on your current HEAD # for example cloning the entire jquery repo locallyīranches and Tags # List all existing branches with the latest commit comment Creating Repositories # create new repository in current directory Trying to remember all those commands to perform common git tasks can be a bit of a nightmare, so we've created this Git cheat sheet of the most common commands so you can print it out as a quick reference to have at your desk. Originally created by Linus Torvalds to help manage the Linux source code, it's now used by millions of projects across all languages. Git is one of the, if the not the, most popular version control systems available.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
